It’s not just men who struggle with body fat measurement. Many women also struggle with measuring their body fat percentage.
Body Fat for Women: Body fat is stored energy used throughout our lives. We need body fat to survive and thrive. When we eat food, some go toward building muscle mass, and some go toward storing energy. Our bodies store excess calories as body fat.
To lose weight, we must burn off more than we take in. If we don’t do any exercise at all, we’ll gain back what we lost. But if we work out regularly, we can reduce our body fat percentage.
There are many alternatives to measuring body fat for women, including using a caliper, bioelectrical impedance analysis, skin fold measurements, and even ultrasound. But these methods aren’t always accurate, especially for women with large breasts and heavy thighs.
In this article, we will cover three new alternative methods for measuring body fat for women. We will compare each method against the traditional “skinfold testing” method and see how well they work. We will also discuss why most alternative methods fail to measure body fat accurately.
The Body Mass Index (BMI) determines whether someone is overweight or obese. You can use the BMI calculator to find your BMI. If you’re underweight, you may need to gain weight, or you may need to lose weight (BMI for Women).
Despite being used for decades as the “go-to” measurement for health based on size, BMI has been widely criticized for oversimplifying what being healthy means.
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is the measurement used to compare your weight to your height (or vice versa).
Drawbacks to the BMI method
However, How often should I weigh myself? Is weighing yourself every day a good idea? What else should I consider before deciding whether or not to weigh myself daily?
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely accepted method for determining one’s risk of developing obesity-related diseases, such as diabetes and heart disease.
Body Mass Index (BMI) is calculated using weight and height measurements. BMI is a ratio of weight to height squared. To calculate BMI, divide weight in kilograms by height in square meters. An ideal body weight range is 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m². Overweight people have BMIs ranging from 25 to 29.9 kg/m^2; heavier people have BMIs more significant than 30 kg/m^2.
While BMI is useful for predicting health risks, it has some limitations. For example, it only considers weight and ignores other important aspects of overall health, such as waist circumference. In addition, BMI fails to distinguish between lean tissue and fat tissue.
Limitations of BMI as a Measure of Body Composition
Many claim BMI is outdated and inaccurate and shouldn’t be used in medical and fitness settings.
BMI (Body Mass Index) is a widely used method for assessing body weight and classifying individuals into underweight, average, overweight, and heavier. However, there are some limitations to using BMI as the sole indicator of health and body composition, leading to its criticism as outdated and inaccurate. Here are some reasons why BMI may be considered obsolete and inaccurate:
Limited Assessment of Body Composition:
BMI is a simple calculation that uses height and weight to estimate body fat. However, it does not differentiate between fat and muscle mass, which can vary significantly among individuals. As a result, individuals with a higher muscle mass, such as athletes or bodybuilders, may be classified as overweight or heavier based on their BMI, even though they have low body fat levels.
Does Not Account for Body Proportions:
BMI does not consider body proportions or variations in fat distribution. For example, individuals with higher muscle mass in the upper body may have a higher BMI due to increased weight. Still, this doesn’t necessarily mean they have excess body fat or the health risks associated with obesity.
Ignores Individual Differences:
BMI does not consider age, gender, bone density, and genetic variations that can influence body weight and composition. As a result, it may not accurately assess specific individuals’ health risks.
Inadequate for Certain Populations:
BMI may not be suitable for specific populations, such as athletes, older adults, or individuals with higher muscle mass or different body proportions. These groups may require more specialized assessments, such as body fat percentage or waist-to-hip ratio, to better evaluate their health status.
Health Risks Vary:
Health risks associated with weight and body composition can differ among individuals. Physical activity level, diet, overall fitness, and medical history significantly determine health outcomes. BMI alone may not capture these crucial factors.
It’s important to note that while BMI has its limitations, it can still give many individuals a general indication of weight status. However, it should be interpreted alongside other assessments, such as body fat percentage, waist circumference, and overall health markers, to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of an individual’s health and risk factors.
So, what is a better measurement?
BMI alternatives
So, what else should you consider besides body fat percentage? Other ways to measure your health include Body Fat Percentage, Waist Circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, etc. These measurements provide a more accurate picture of your health.
It has been suggested that WHR is a better indicator of health risk than BMI because it takes body shape into account. For example, women who carry excess weight around their middle tend to store more fat around their hips than around their waist. In contrast, men with large bellies often have less fat around their midsection than around their hips.
Body Fat Percentage
The first alternative, Body fat percentage, is the relative amount of body fat a person has.
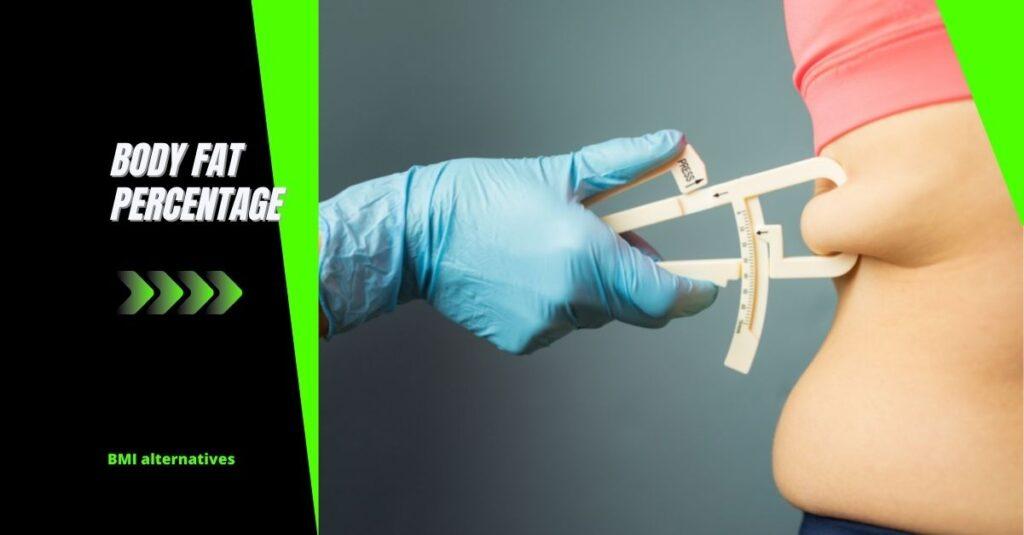

Body fat percentage measures the amount of fat stored in your body. It is calculated using a particular caliper that measures the circumference of your arms, legs, chest, and stomach. These measurements are added and divided by 4 to get the total body fat percentage. Body fat percentage is a more accurate representation than BMI because it considers the amount of muscle you have.
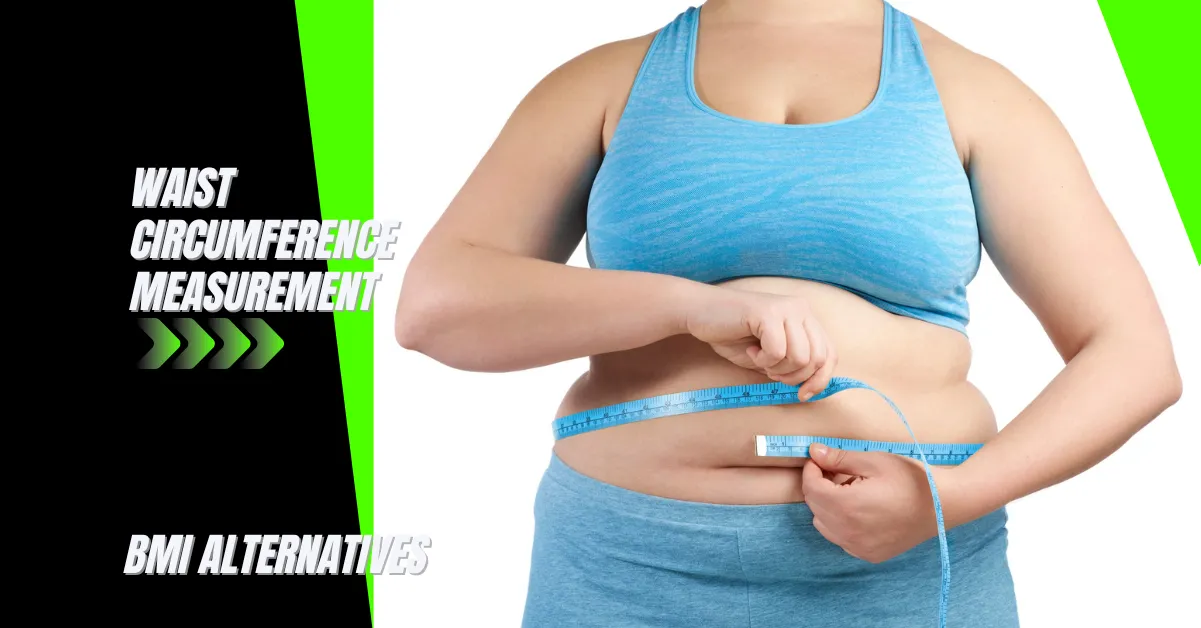
Waist Circumference Measurement
The circumference of the waist can be used as a BMI alternative even without a hip measurement; this is useful for individuals who are obese or otherwise have difficulty making a hip measurement. Given the health risks associated with having a high percentage of abdominal fat, measuring waist circumference can give you an idea of whether you are at risk.
- Use a measuring tape.
- Surround the measuring tape at the natural waist, between the lowest rib and the top of the hip bone, or at the navel button.
- The waist circumference (WC) measures around the most comprehensive portion of the abdomen at the level of the umbilicus. A standard WC ranges between 35 inches and 40 inches. If it exceeds 40 inches, it indicates obesity.
According to the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, women with a waist circumference of over 35 inches and men with a waist circumference of over 40 inches have an increased risk of developing heart disease and Type 2 diabetes.
Waist to Hip Ratio
What is the waist-to-hip ratio (WHR)? Is it essential to measure it? And why should I care?
Waist-to-height ratios measure the proportion of fat stored in the abdominal region compared to total body size. Abdominal fat stores are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and diabetes.
WHR is calculated by dividing the waist measurement by the height. A high WHR means that the person’s waistline is larger relative to his or her height. This number helps determine whether or not you are at risk for developing diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, stroke, and other health conditions.
Assessing Body Fat Distribution: Waist-to-Hip Ratio as a Tool
A higher WHR means your body fat distribution is concentrated around your middle. Lowering your WHR can reduce your risk of these diseases.
Calculating Waist-to-Hip Ratio: A Simple and Effective Method
A measurement of the waist is taken at either the minor point of the waist or just above the belly button and divided by a measurement of the widest part of the hips; results larger than 0.85 for women or 0.9 for men indicate abdominal obesity.
Measure the waist circumference.
- Measure the hip at its widest diameter.
- Divide waist measurement by hip measurement.
| WHR for women | Health risks for obesity-related conditions |
| 0.8 or lower | Low |
| 0.81 to 0.84 | Moderate |
| 0.85 or higher | High |
Calculator - Waist Circumference Measurement
Hip Circumference (HC)
Hip circumference is a measurement taken around the widest part of the hips. It is commonly used in conjunction with waist circumference to calculate the waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), which is a valuable indicator of body fat distribution and overall health. Hip circumference measures around the fullest part of the buttocks. The average hip circumference ranges between 34 inches and 38 inches. If the HC exceeds 39 inches, then it indicates overweight.
Does BMI Apply Differently to Black Women and People of Color?
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used screening tool, but its accuracy in estimating body fat percentage and health risk varies significantly across different racial and ethnic groups. This is a crucial point often overlooked in general health discussions.
The BMI was initially developed in the 19th century based on data primarily from European populations, making its direct application to a globally diverse population inherently problematic.
Understanding BMI’s Origins and Limitations
The BMI was conceived in the 19th century by Adolphe Quetelet, a Belgian mathematician, not a physician. It was developed to provide a quick statistical measure of body mass across populations, not to assess individual health or body fat composition. While convenient, its widespread adoption in clinical settings has often overshadowed its inherent limitations, particularly regarding body composition.
Key Differences Across Populations
Asian Populations and “Normal Weight Obesity”
On average, individuals of Asian descent tend to have a higher body fat percentage at lower BMI values compared to White individuals. This phenomenon, sometimes called “normal weight obesity” or “thin outside, fat inside,” means they can be at increased risk for conditions like type 2 diabetes even with a “normal” BMI.
For example, the World Health Organization (WHO) and other health bodies recommend lower BMI cut-offs for Asian populations: a BMI of 23 kg/m² or higher is often considered overweight, and 25 kg/m² or higher as obese, in contrast to the standard 25 kg/m² for overweight and 30 kg/m² for obesity for Caucasian populations. Studies show Asians can have 2-3 kg/m² lower BMI than Caucasians for the same body fat level.
Black Women: Higher BMI, Different Body Composition
Research consistently shows that Black women tend to have higher average BMIs than White women. However, this often correlates with a higher lean body mass (muscle and bone density) rather than proportionally more body fat. For instance, a 2011 study in the International Journal of Obesity noted that Black women, on average, have about 3% to 6% lower body fat percentage than White women at the same BMI.
This suggests that the standard body mass index calculation might overestimate body fat levels and associated health risks in Black women. The CDC’s 2017-2018 data showed the age-adjusted prevalence of obesity was highest among non-Hispanic Black adults (49.6%) compared to non-Hispanic White (42.2%), Hispanic (44.8%), and non-Hispanic Asian (17.4%) adults. Specifically, non-Hispanic Black women had a higher prevalence of obesity (56.9%) than non-Hispanic Black men (41.1%).
Other Ethnically Diverse Populations
Beyond Asian and Black populations, other groups also exhibit unique body composition characteristics. For example, a study highlighted that the BMI likely overestimates overweight and obesity in the Inuit population. This is attributed to their distinct body composition, which often includes a greater lean body mass relative to their height and a different body build (e.g., shorter legs relative to torso length).
Similarly, Hispanic and Indigenous populations may also present different body fat distributions and lean body mass compared to the general population used for BMI’s original calibration.
Source and Credits:
Weight Loss Made Easy: Lose Weight Calculator
Obesity Is Bad, But Did You Know It Also Impacts Your Heart?
https://www.medicinenet.com/is_there_a_better_alternative_to_measuring_bmi/article.htm
https://healthyliving.azcentral.com/correlation-between-arm-length-leg-length-11071.html
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/bmi-for-black-women

BMI Index Calculator

Basal Metabolic Rate

Tdee Calculator


I’ve been focusing on my waist-to-hip ratio lately, as I’ve heard it’s a better indicator of abdominal fat and health risks. Thanks for breaking down the differences between these methods. Knowledge is power!
BMI has always felt limiting and inaccurate to me, so I’m thrilled to see a discussion about better alternatives. It’s important to consider a person’s overall health and not just a number on a scale
Great post! I always thought BMI was the most accurate way to measure body fat. This comparison really opened my eyes to the importance of waist-to-hip ratio. Thanks for sharing!
Great post! BMI is a flawed measurement. It doesn’t account for factors like muscle mass and body composition. Body composition analysis and waist-to-hip ratio are much better indicators of overall health