Understanding the Relationship Between Obesity, BMI Index, and Heart Disease
The Body Mass Index (BMI) measures body fat based on a person’s weight and height. A BMI of 25 or higher is considered overweight, and a BMI of 30 or higher is considered obese. Obesity is defined as an excessive amount of body fat.
-
Understanding the Relationship Between Obesity, BMI Index, and Heart Disease
- Everything You Need To Know About Weight, Health, And BMI Index
- Obesity classes:
- Understanding and Measuring Body Fat Percentage: A Comprehensive Guide
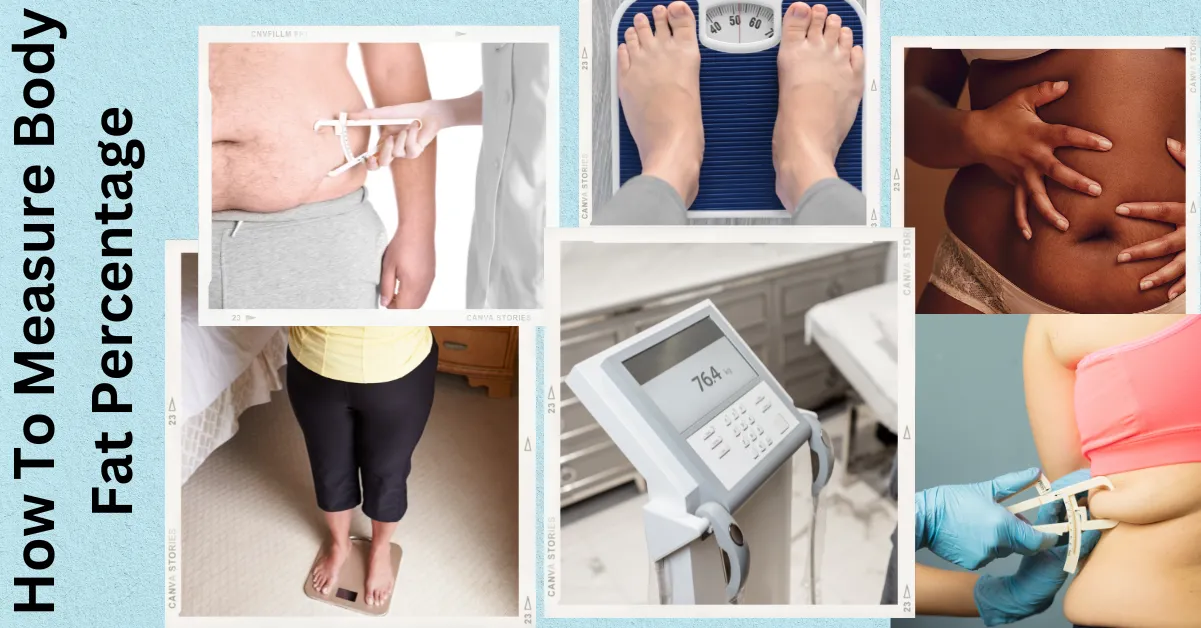
- How To Measure Body Fat Percentage
- Comprehensive Health and Fitness Toolkit - Waist-to-Hip Ratio and BMI Index: What You Need to Know
- Source & Credits
Obesity is a significant risk factor for heart disease. When a person is obese, they are more likely to have high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes, all of which are known risk factors for heart disease. In addition, obesity can cause inflammation in the body, which can further increase the risk of heart disease.
Obesity is also linked to other health problems, such as sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis.
It’s worth noting that BMI is not always an accurate measure of a person’s health. It doesn’t consider muscle mass, bone density, and fat distribution factors. Therefore, it should not be used as a diagnostic tool.
To determine if a person is at risk for heart disease, healthcare professionals consider various factors, including BMI, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and family history. They may also use other measurements, such as waist circumference and skinfold thickness, to determine a person’s body fat percentage.
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular physical activity, a nutritious diet, and not smoking, can help reduce the risk of heart disease and obesity.
Everything You Need To Know About Weight, Health, And BMI Index
Obesity classes:
Many BMI calculators available online will allow you to check your BMI. The table for determining risk factors associated with obesity is as follows:
- Below 18.5 – Underweight
- 18.5 – 24.9 – Normal
- 25.0 – 29.9 – Overweight
- 30.0 – 39.9 – Obese
- 40 – Up – Morbidity Obese
Consequently, if your BMI is above 25.0, you should know that losing even a moderate amount of weight has great benefits.
Understanding and Measuring Body Fat Percentage: A Comprehensive Guide
Body fat measurement refers to the assessment of the amount of fat in the body. It’s an important aspect of health and fitness because it can help determine whether a person is at a healthy weight. Here are some key points to understand:
What is Body Fat? Body fat protects your organs, stores energy, and regulates your hormones and body temperature. However, too much body fat, especially around the waist, can increase the risk of health problems like heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Body Fat Percentage: This is the total mass of fat divided by total body mass times 100. It includes essential body fat and storage body fat. Essential body fat is necessary to maintain life and reproductive functions, while storage body fat consists of fat accumulation in adipose tissue.
Methods of Measurement: There are several ways to measure body fat, including skinfold thickness measurements, bioelectrical impedance, dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), and hydrostatic body fat measurement. Each method has its pros and cons regarding accuracy, cost, and convenience.
Healthy Body Fat Ranges: Healthy body fat percentages can vary based on age, sex, and health. For example, a body fat percentage of 6-24% is generally considered healthy for men, while for women, a percentage of 16-30% is considered healthy. However, these ranges can vary depending on the source.
Body Mass Index (BMI) vs. Body Fat Percentage: While BMI allows for quick comparisons across large populations, it doesn’t directly measure body fat. It’s possible for a person to have a healthy BMI but still have too much body fat, or vice versa. Therefore, measuring body fat can provide a more accurate picture of a person’s health.
How To Measure Body Fat Percentage
There are several methods to measure body fat percentage, each with varying degrees of accuracy and convenience. Here are some of the most common methods:
Skinfold Calipers: This method involves using calipers to measure the thickness of skinfolds at various parts of the body. These measurements are then used to estimate total body fat. While this method can be reasonably accurate when done by a trained professional, it can be less accurate when done by an untrained individual.
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA): This method involves sending a small electrical current through the body and measuring the resistance to this current. Fat, water, and muscle in the body all conduct electricity differently, so this method can be used to estimate body fat percentage. Many modern scales and fitness devices include BIA technology.
Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA): This method involves using a machine that produces two different X-ray beams, which are used to measure bone density and the amounts of fat and muscle in the body. It is very accurate but can be expensive and is not as readily available as some other methods.
Hydrostatic Weighing: This method involves weighing a person in and out of water. Because fat is less dense than water, a person with more body fat will weigh less in water compared to a person with less body fat. This method is very accurate but inconvenient and is typically only available in particular research or clinical settings.
Air Displacement Plethysmography (Bod Pod): This method involves sitting in a small chamber (the Bod Pod) that measures your weight and volume to determine your body density. From this, your body fat percentage can be estimated. This method is accurate but expensive and is not as widely available as other methods.
3D Body Scanners: These use infrared sensors to capture the shape of your body and then calculate body measurements and body fat percentage. They are becoming more common in fitness centers and medical settings.
Comprehensive Health and Fitness Toolkit – Waist-to-Hip Ratio and BMI Index: What You Need to Know
Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) Calculator: This tool would calculate the total number of calories a person needs to consume in a day, considering their BMR and their level of physical activity. After calculating their BMR, this would be a natural next step for users, giving them a more accurate picture of their daily caloric needs.
Macronutrient Calculator: This tool would provide users with a breakdown of the grams of protein, carbohydrates, and fats they should consume daily based on their caloric needs. It would be helpful for users interested in more detailed diet planning.
Body Mass Index (BMI) Calculator: This tool calculates a person’s BMI, which measures body fat based on height and weight. Although it has limitations, BMI can be a useful initial indicator of whether a person is underweight, healthy, overweight, or obese.
Fitness Tracker: This tool would allow users to log their workouts and track the number of calories they burn through exercise. This would be useful for users trying to lose or maintain a healthy weight, as it would help them ensure they are burning more calories than they consume.
Meal Planner: This tool would help users plan meals that meet their caloric and macronutrient needs. It could suggest recipes based on the user’s dietary preferences and nutritional needs.
Hydration Tracker: Staying hydrated is an essential part of overall health. This tool would remind users to drink enough water throughout the day.
- Waist Circumference Measurement: Waist circumference measurement is a simple and effective way to assess abdominal obesity and associated health risks. Healthcare providers can determine if a person carries excess fat around their midsection by measuring the waist circumference, typically at the navel level.





Take control of your heart health by managing your BMI. Discover why maintaining a healthy BMI is crucial for your heart and how to achieve it.
The key to maintaining a healthy BMI is to make sustainable lifestyle changes. This includes eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, managing stress, and getting enough sleep. It’s not about perfection, but progress. Every small step you take towards a healthier lifestyle counts!
Es impresionante cómo la conexión entre la obesidad, el IMC y la salud del corazón es tan estrecha y compleja. Agradezco mucho la información detallada y los consejos prácticos para cuidar de nuestro corazón a través de una mejor nutrición y ejercicio.
Understanding your BMI is a crucial step in maintaining a healthy heart! It’s great to see more awareness being raised about this important aspect of overall health.
It’s important to remember that weight loss is a journey, not a race. Small steps can lead to big changes. Focus on making sustainable lifestyle modifications, and celebrate your successes, no matter how small